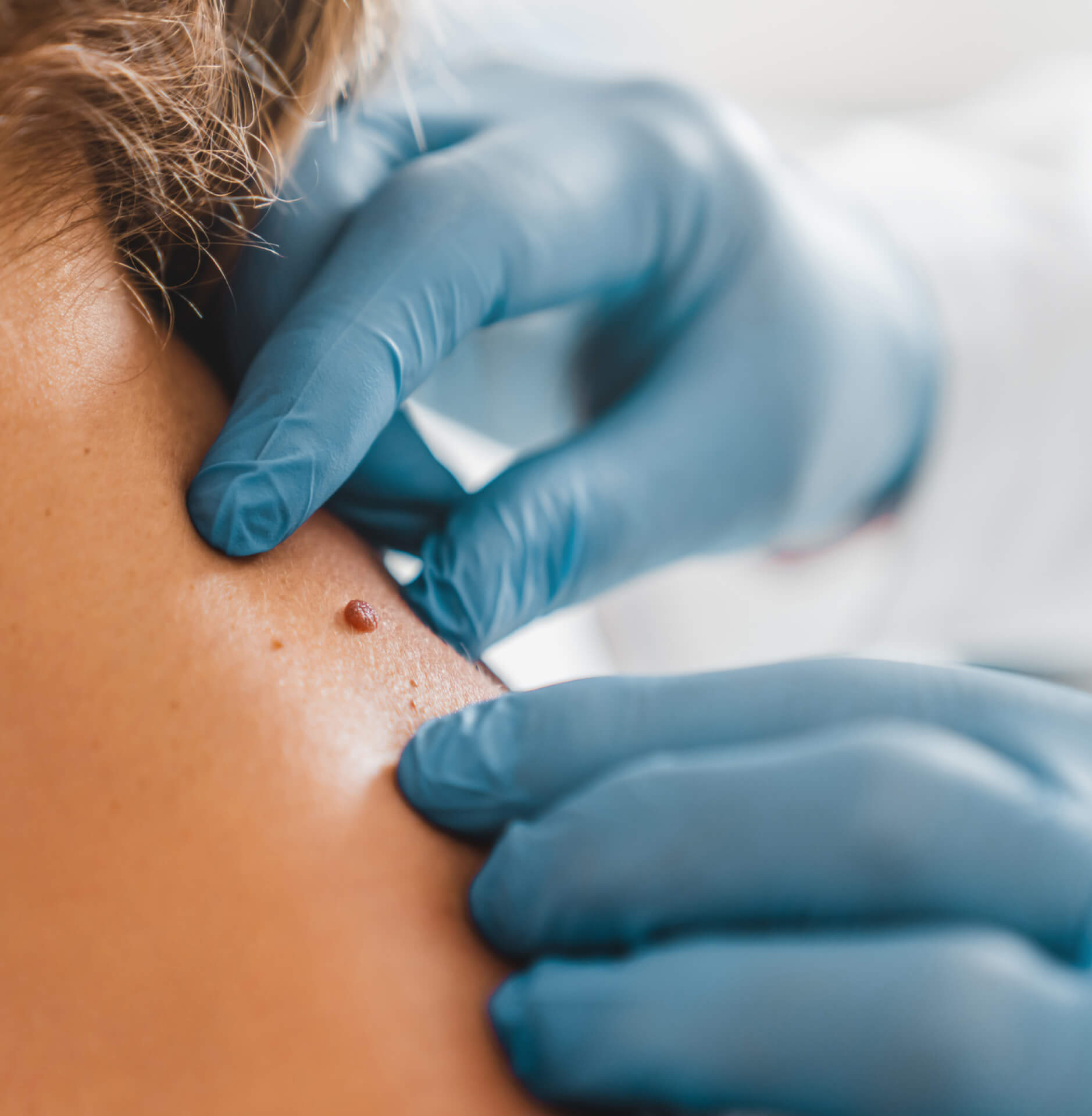
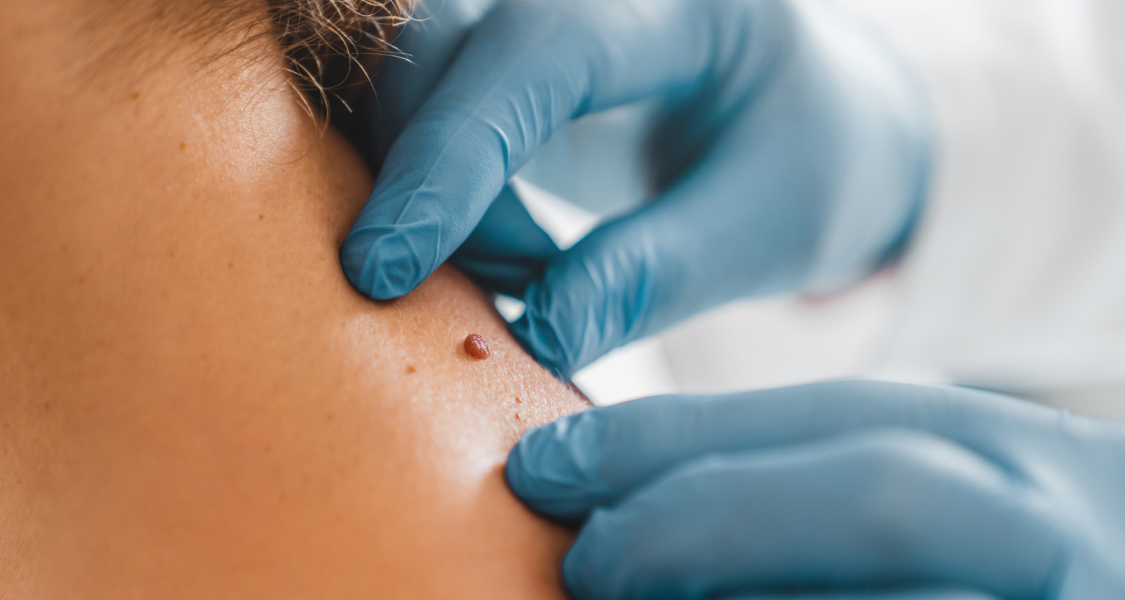
Symptoms of Melanoma Skin Cancer
The first sign of melanoma is often a new mole or a change in the appearance of an existing mole.
Here are some ways you can identify a melanoma:
-
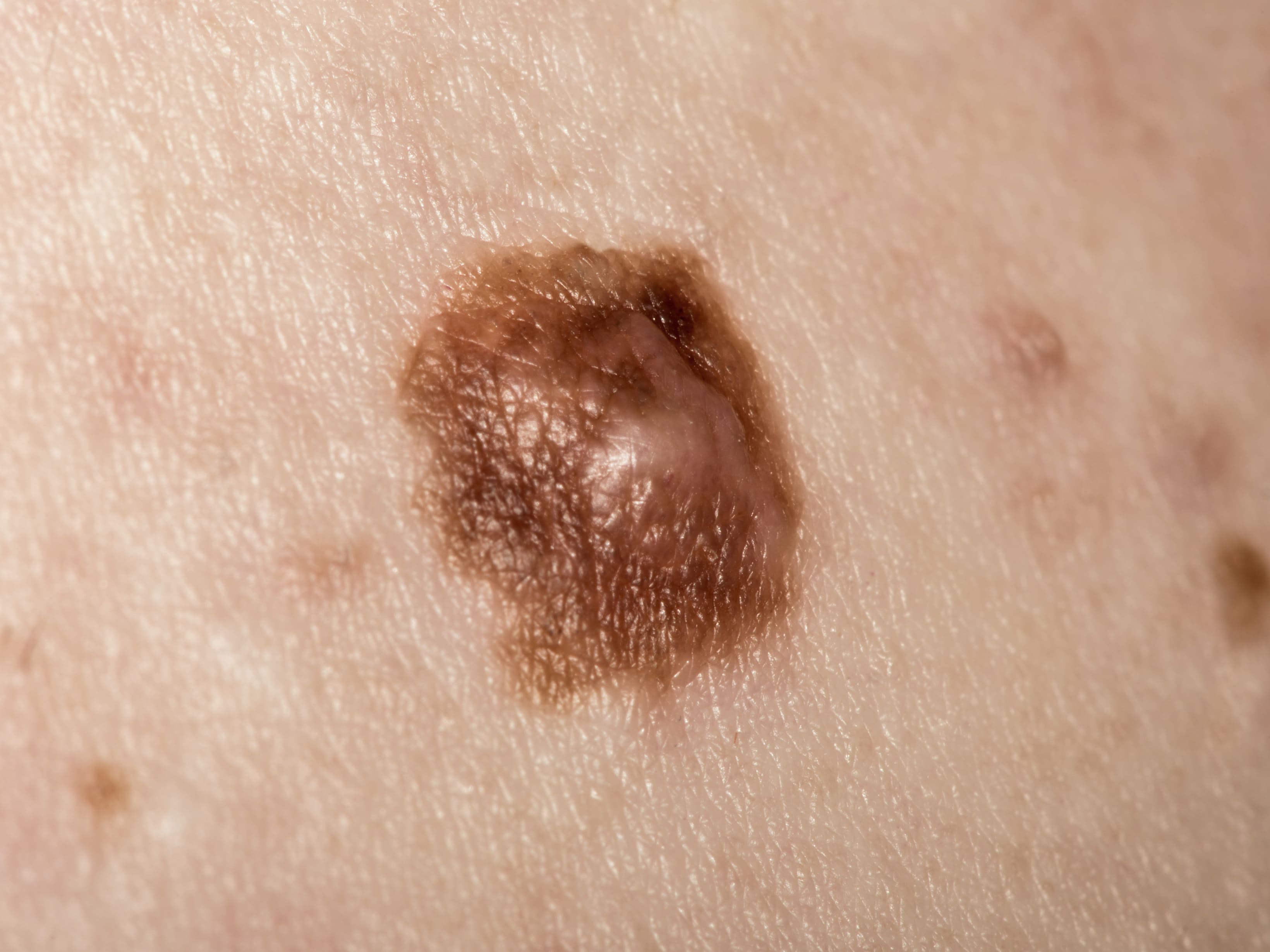
Asymmetrical Shape
Melanomas typically have 2 very different halves and are an irregular shape.
-
Notched or Ragged Border
Melanomas usually have a notched or ragged border.
-
Mixed Colour
Melanomas are typically a mix of 2 or more colours.
-
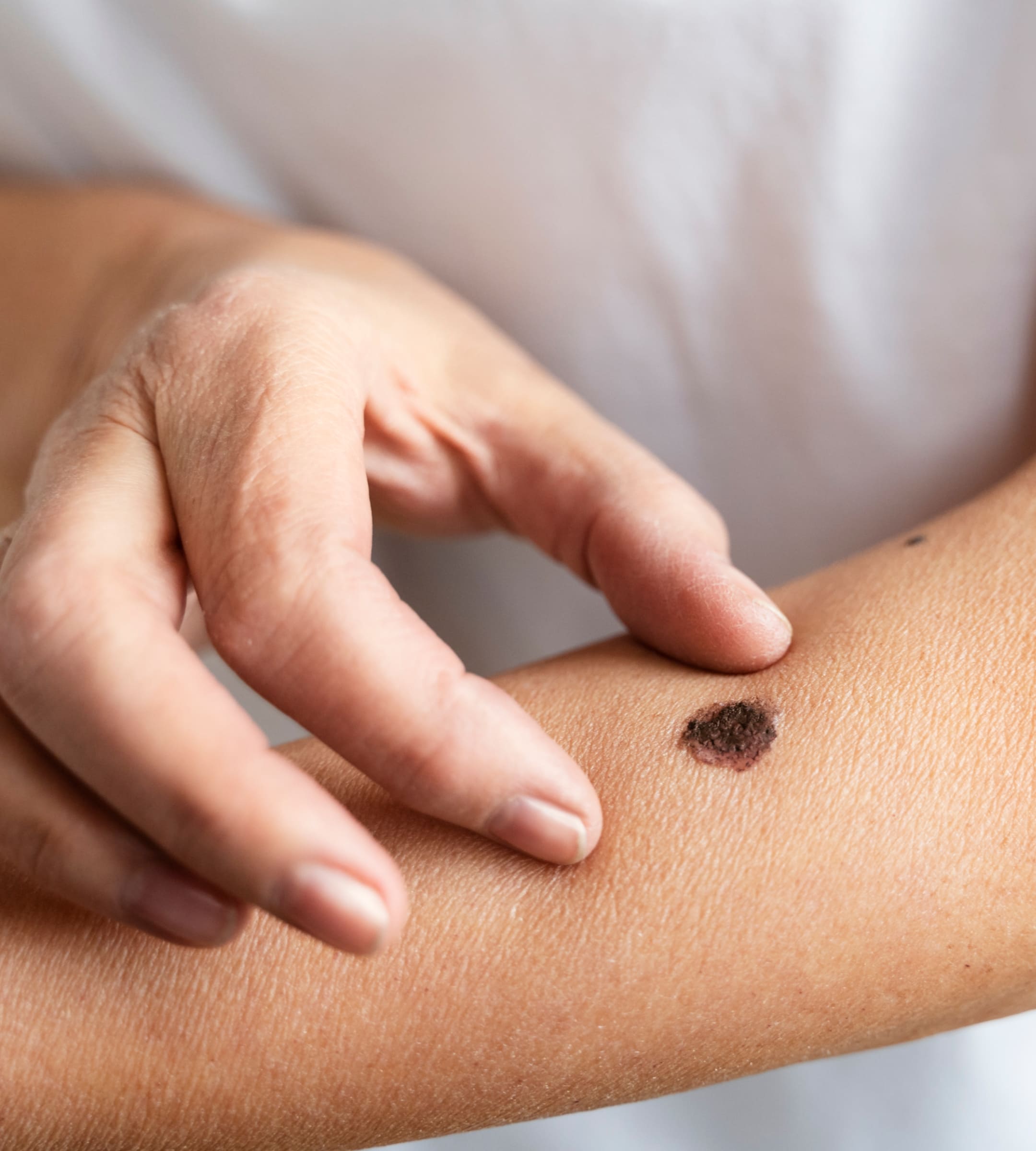
Large Diameter
Most melanomas are usually larger than 6mm in diameter.
-
Enlargement or Elevation
A mole that changes its overall size over time is more likely to be a melanoma.