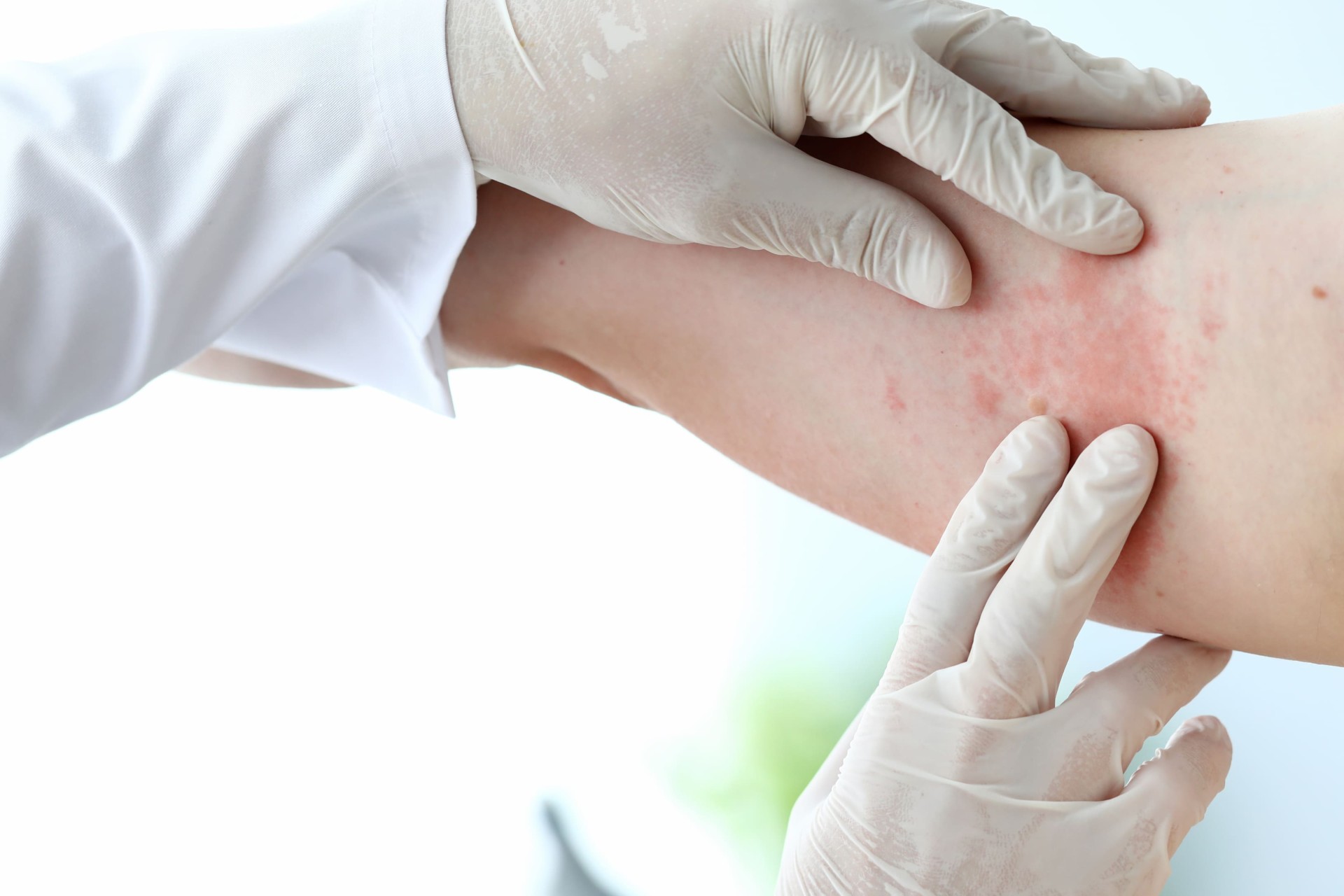
Introduction
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a skin condition characterised by itchy and swollen red bumps on the skin, and can be triggered by a variety of factors, ranging from allergic reactions to stress. Hives can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, causing discomfort and affecting the quality of your life.
By identifying and avoiding triggers, you can reduce the frequency and severity of hives outbreaks. In this article, we will explore the common causes and triggers of hives.
Allergic Causes of Hives
In an allergic reaction, the immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless substance.
This leads to the release of histamine, which causes the blood vessels in the skin to dilate and become leaky, resulting in the characteristic redness, swelling, and itching of hives. Hives can be caused by a variety of allergic triggers, including:
- Foods: Certain foods, such as nuts, shellfish, and eggs.
- Medications: Some medications, including antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Insect bites or stings: Hives can develop in response to bites or stings, particularly from bees or wasps.
- Latex: You may develop hives after coming into contact with latex.
- Pet dander: Exposure to pet dander, particularly from cats and dogs, can cause hives for some people.
Non-allergic Causes of Hives
Similar to allergic triggers, non-allergic triggers, such as stress or changes in temperature can also cause flare-ups.
- Stress: Emotional stress can trigger the release of chemicals in the body that cause hives to develop.
- Temperature changes: Exposure to extreme temperatures, such as hot or cold weather or a hot shower.
- Exercise: Vigorous exercise can cause hives to develop in some.
- Pressure: Pressure on the skin, such as from tight clothing or a tight seatbelt.
- Sunlight: Exposure to sunlight, particularly in individuals with photosensitivity.
Factors Contributing to the Risk of Developing Hives
While hives can occur in anyone, there are several factors that may increase an individual’s risk of developing hives, including:
- Genetics: Hives can run in families.
- Age: Hives are more common in children and young adults.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop hives than men.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or viral infections, can increase the risk of developing hives.
- Certain medications: Some medications, including antibiotics and pain relievers, can increase the risk of developing hives as a side effect.
These factors may increase an individual’s risk of developing hives, however, it is a condition that can occur in anyone, regardless of age, gender, or medical history.
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Strategies to Minimize a Hives Outbreak
While hives can be challenging to manage, there are several strategies that can help minimize the frequency and severity of hives outbreaks, including:
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as certain foods or medications, can reduce the risk of outbreaks.
- Stress management: Practicing stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help reduce emotional stress.
- Temperature regulation: Avoiding extreme temperatures, such as hot or cold weather, can minimize outbreaks triggered by changes in temperature.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothing can minimize outbreaks triggered by pressure on the skin.
- Keeping skin moisturized: Keeping the skin moisturized can help reduce dryness and itchiness, which can exacerbate hives symptoms.
- Seeking medical treatment: If hives outbreaks are frequent or severe, medical treatment prescribed by a dermatologist may be necessary to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Hives are a common skin condition that can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergies, stress, and changes in temperature. While hives can be uncomfortable and even debilitating in severe cases, managing symptoms and avoiding triggers can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Seek medical treatment when necessary, individuals with hives can take control of their condition and improve their quality of life. If you are experiencing symptoms of hives, consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.